阿卡波糖片(Acarbose)说明书
产地国家:欧洲共同体国家 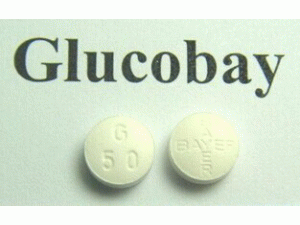 处 方 药:是
所属类别:50毫克/片 100片/盒
包装规格:50毫克/片 100片/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:拜耳
生产厂家英文名:QUIMICA FARMACEUTICA BAYER S.L.
原产地英文商品名:GLUCOBAY 50MG/TAB 100TABS/BOX
原产地英文药品名:ACARBOSE
中文参考商品译名:拜唐苹 50毫克/片 100片/盒
中文参考药品译名:阿卡波糖
处 方 药:是
所属类别:50毫克/片 100片/盒
包装规格:50毫克/片 100片/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:拜耳
生产厂家英文名:QUIMICA FARMACEUTICA BAYER S.L.
原产地英文商品名:GLUCOBAY 50MG/TAB 100TABS/BOX
原产地英文药品名:ACARBOSE
中文参考商品译名:拜唐苹 50毫克/片 100片/盒
中文参考药品译名:阿卡波糖
 处 方 药:是
所属类别:50毫克/片 100片/盒
包装规格:50毫克/片 100片/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:拜耳
生产厂家英文名:QUIMICA FARMACEUTICA BAYER S.L.
原产地英文商品名:GLUCOBAY 50MG/TAB 100TABS/BOX
原产地英文药品名:ACARBOSE
中文参考商品译名:拜唐苹 50毫克/片 100片/盒
中文参考药品译名:阿卡波糖
处 方 药:是
所属类别:50毫克/片 100片/盒
包装规格:50毫克/片 100片/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:拜耳
生产厂家英文名:QUIMICA FARMACEUTICA BAYER S.L.
原产地英文商品名:GLUCOBAY 50MG/TAB 100TABS/BOX
原产地英文药品名:ACARBOSE
中文参考商品译名:拜唐苹 50毫克/片 100片/盒
中文参考药品译名:阿卡波糖
简介
部分中文拜唐苹处方资料(仅供参考) 拜唐苹Glucobay 中文别名:阿卡波糖、阿卡波糖,拜糖平 英文别名:Acarbose 生产企业:德国拜耳 药品类别:胰腺激素及其它影响血糖药 性 状 为一种新型口服降糖药。 药理药动 本品是一个α-糖苷酶抑制剂。它结合于碳水化合物分解酶(α-糖苷酶),从而竞争性和可逆性地抑制了小肠中碳水化合物的分解,使糖的吸收相应减缓,因而拜糖平可以减少饭后血糖浓度的增高。由于小肠内糖吸收的减缓和大肠内糖的调节吸收,使一天内血糖浓度平稳,平均值下降。拜糖平对非胰岛素依赖型糖尿病人单独治疗有明显疗效,可降餐后血糖和空腹血糖。它也适合与其它日服胶降糖药合用,临床试验1年结果,拜糖平对55%已服磺脲类药物的病人和的%已服双胍类药物的病人,均有明显的作用。 适 应 症 非胰岛素依赖型糖尿病人,当单纯饮食治疗不能控制血糖时,拜糖平应用作一线治疗药。 当现有常规降糖药不能正常控制代谢状态时,拜糖平可加入合并使用。 胰岛素依赖型糖尿病人可配合胰岛素合并使用。 用法用量 每片50mg,初起量为1天3次每次一片,以后可增加到一天3次每次2片。 不良反应 因糖类在小肠内分解及吸收缓慢,停留时间延长,经肠道细菌的酵解而产气增多,因此可引起腹胀、腹痛及腹泻等。 也可引起低血糖。 禁忌症 禁用于对阿卡波糖的过敏反应者; 也不能用于18岁以下的病人; 有明显消化、吸收障碍的慢性肠功能紊乱; 禁用于肠胀气面可能恶化的情况(如严重的疝气、肠梗阻和肠溃疡等)。 孕妇及哺乳期妇女用药 怀孕期间禁服拜糖平,哺乳期也不要服用拜糖平。英文版说明书
GLUCOBAY® 50, 100 SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): GLUCOBAY® 50, 100 Tablets COMPOSITION: GLUCOBAY 50 tablets contain 50 mg acarbose GLUCOBAY 100 tablets contain 100 mg acarbose PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION: A 21.2 Oral hypoglycaemics PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION: GLUCOBAY is a competitive inhibitor of intestinal alpha-glucosidases with maximum specific inhibitory activity against sucrose. Under the influence of GLUCOBAY, the digestion of starch and sucrose into absorbable monosaccharides in the small intestine is dose-dependently delayed. In diabetic subjects, this results in a lowering of postprandial hyperglycaemia. GLUCOBAY has no stimulatory action on the pancreas. Treatment with GLUCOBAY also results in a reduction of fasting blood glucose and to modest changes in levels of glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1, HbA1c). The changes may be a reduction or reduced deterioration in HbA1 or HbA1c levels, depending upon the patient's clinical status and disease progression. These parameters are affected in a dose-dependent manner by GLUCOBAY. Following oral administration, only 1-2% is absorbed. INDICATIONS: GLUCOBAY is indicated for the treatment of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in patients inadequately controlled on diet alone, or on diet and oral hypoglycaemic agents. CONTRA-INDICATIONS: Known hypersensitivity to acarbose or any of the excipients, use in children less than 12 years of age, pregnancy and in nursing mothers. GLUCOBAY is also contra-indicated in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, colonic ulceration, partial intestinal obstruction or in patients predisposed to intestinal obstruction. In addition, GLUCOBAY should not be used in patients who have chronic intestinal diseases associated with marked disorders of digestion or absorption and in patients who suffer from states which may deteriorate as a result of increased gas formation in the intestine, (e.g. Roemheld’s syndrome [an angina pectoris-like syndrome or aggravation of an angina pectoris due to the post-prandial filling of the stomach] and larger hernias). GLUCOBAY is contra-indicated in patients with hepatic and severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <25 mL/min/ 1,73m2). WARNINGS: Hypoglycaemia: When administered alone, GLUCOBAY does not cause hypoglycaemia. It may, however, act to potentiate the hypoglycaemic effects of insulin, metformin and/or sulphonylurea drugs and the dosages of these agents may need to be modified accordingly. In the management of episodes of hypoglycaemia occurring during therapy, it is essential that glucose and not sucrose is used. This is because acarbose will delay the digestion and absorption of disaccharides, but not monosaccharides. Transaminases: At higher doses, GLUCOBAY may give rise to transient idiosyncratic elevations of serum hepatic transaminases. Asymptomatic liver enzyme elevations may occur. Therefore, liver enzyme monitoring should be considered during the first 6 to 12 months of treatment. Patients titrated to the maximum recommended dose of 200 mg three times a day should be closely monitored, preferably at monthly intervals for the first six months. If elevated transaminases are observed, a reduction in dosage or withdrawal of therapy may be warranted, particularly if the elevations persist. In such circumstances, patients should be monitored at weekly intervals until normal values are established. In eva luable cases these changes were reversible on discontinuation of Glucobay therapy. Interactions: Intestinal adsorbents (e.g. charcoal) and digestive enzyme preparations containing carbohydrate splitting enzymes (e.g. amylase, pancreatin) may reduce the effect of GLUCOBAY and should not therefore be taken concomitantly. The concomitant administration of neomycin may lead to enhanced reductions of postprandial blood glucose and to an increase in the frequency and severity of gastrointestinal side-effects. If the symptoms are severe, a temporary dose reduction of GLUCOBAY may be warranted. The concomitant administration of cholestyramine may enhance the effects of GLUCOBAY, particularly with respect to reducing postprandial insulin levels. In the rare circumstance that both acarbose and cholestyramine therapy are withdrawn simultaneously, care is needed as a rebound phenomenon has been observed with respect to insulin levels in non-diabetic subjects. In a pilot study to investigate a possible interaction between GLUCOBAY and nifedipine, no significant or reproducible changes were observed in the plasma nifedipine profiles. Acarbose may affect digoxin bioavailability, which may require dose adjustment of digoxin. The concomitant administration of metformin, sulphonylureas and/or insulin may enhance the antihyperglycaemic effects of GLUCOBAY. Hypoglycaemic shock may thus occur less frequently in patients taking these combinations. DOSAGE AND DIRECTIONS FOR USE: GLUCOBAY tablets are taken orally and should be chewed with the first mouthful of food, or swallowed whole with a little liquid directly before the meal. Owing to the great individual variation of glucosidase activity in the intestinal mucosa, there is no fixed dosage regimen, and patients should be treated according to clinical response and tolerance of intestinal side-effects. Adults: The recommended initial dose is 50 mg three times a day. If after six to eight weeks treatment patients show an inadequate clinical response, the dosage may be increased to 100 mg three times a day. A further increase in dosage to a maximum of 200 mg three times a day may occasionally be necessary. GLUCOBAY is intended for continuous long-term treatment. Elderly patients: No modification of the normal adult dosage regimen is necessary. SIDE EFFECTS AND SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS: Owing to its mode of action, GLUCOBAY results in a greater proportion of dietary carbohydrate being digested in the large bowel. This carbohydrate may also be utilised by the intestinal flora, resulting in the increased formation of intestinal gas. Flatulence, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, borborygmi and a feeling of fullness. Subileus/ileus may occur. If the prescribed diabetic diet is not adhered to the intestinal side effects may be intensified. If strongly distressing symptoms develop in spite of adherence to the diabetic diet prescribed, the doctor must be consulted and the dose temporarily or permanently reduced. The symptoms are both dose and dietary substrate related and may subside with continued treatment. Symptoms can be reduced by adherence to the prescribed diabetic diet and the avoidance of sucrose or foodstuffs containing sugar. If symptoms are poorly tolerated, a reduction in dosage is recommended. Should diarrhoea persist, patients should be closely monitored and the dosage reduced, or therapy withdrawn, if necessary. The administration of antacid preparations containing magnesium and aluminium salts has been shown not to ameliorate the acute gastrointestinal symptoms of GLUCOBAY in higher dosage and should therefore not be recommended to patients for this purpose. In individual cases, hypersensitive skin reactions may occur e.g. rash, erythema, exanthema and urticaria. Cases of jaundice and/or hepatitis, clinically relevant abnormal liver function tests (three times above upper limit of normal range) and associated liver damage have been reported less frequently. Abnormal values may be transient under ongoing Acarbose therapy (See Warnings). Oedema has been observed less frequently. KNOWN SYMPTOMS OF OVERDOSAGE AND PARTICULARS OF ITS TREATMENT: No information on overdosage is available. No specific antidotes to GLUCOBAY are known. Intake of carbohydrate-containing meals or beverages should be avoided for 4-6 hours. Diarrhoea should be treated by standard measures. IDENTIFICATION: GLUCOBAY 50: Round, convex white to yellow tinged tablets with G 50 on the upper side and the BAYER cross on the lower side. GLUCOBAY 100: Round, convex, scored white to yellow tinged scored tablets with G 100 on the upper side and the BAYER cross on the lower side. PRESENTATION: GLUCOBAY 50: Blister packs of 90 tablets GLUCOBAY 100: Blister packs of 90 tablets STORAGE INSTRUCTIONS: Store below 25°C. Protect from moisture. Keep out of reach of children. At higher temperatures and/or higher relative humidity, discolouration can occur in tablets that are not in the packs (blisters). Tablets should therefore not be removed from the foil until immediately prior to use. REGISTRATION NUMBER: ZIMBABWE ONLY GLUCOBAY 50: 28/21.2/0425 2000/17.7/3650 GLUCOBAY 100: 28/21.2/0426 2000/17.7/3649 NAME AND BUSINESS ADDRESS OF THE APPLICANT用药温馨提示:当您服用此药物时,需定期接受医疗专业人士的检查,以便随时针对其药效、副作用等情况进行监测。本网站所包含的信息旨在为患者提供帮助,不能代替医学建议和治疗。
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 阿卡波糖片(Acarbose)说明书
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 阿卡波糖片(Acarbose)说明书


